The Moyno Pump Curve is a fundamental resource for understanding the operational performance of Moyno progressive cavity pumps. This guide will provide an in-depth look at what a pump curve is, how to read it, and its significance in pump selection and application.
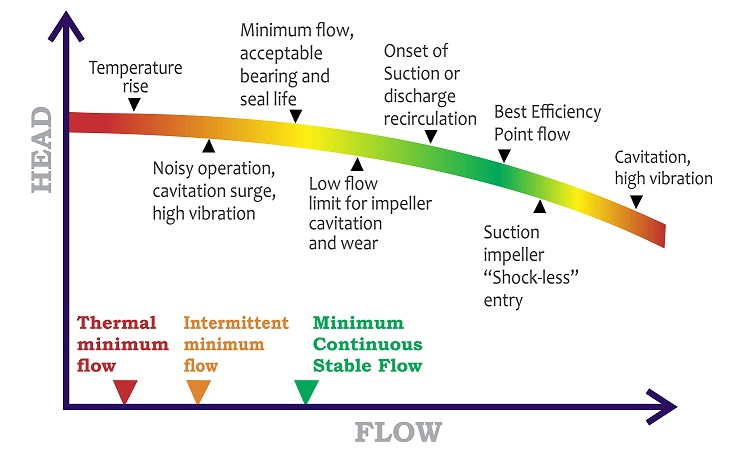
What is a Pump Curve?
A pump curve is a graphical representation that illustrates the relationship between the flow rate and the head (pressure) produced by a pump. It serves as a vital tool for engineers and operators to assess pump performance.
Key Components of a Pump Curve:
- Flow Rate (Q):
- Measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM).
- Typically represented on the X-axis of the graph.
- Head (H):
- Measured in feet or meters.
- Indicated on the Y-axis, showing the pressure the pump can generate.
- Efficiency Curve:
- Displays the efficiency of the pump at various flow rates.
- Typically shown as a separate line on the graph.
- Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHr):
- Indicates the minimum pressure required to prevent cavitation in the pump.
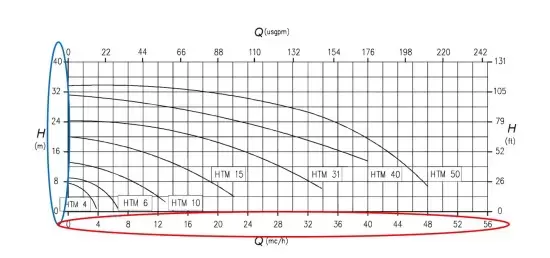
How to Read the Moyno Pump Curve
- Identify the Axes:
- The X-axis represents the flow rate.
- The Y-axis represents the head (pressure).
- Locate the Operating Point:
- Find the desired flow rate on the X-axis.
- Draw a vertical line up to the pump curve to determine the corresponding head.
- Evaluate Efficiency:
- Identify the efficiency line on the curve.
- Determine the pump’s efficiency at the operating point to ensure it is within the optimal range.
- Check NPSHr:
- Make sure that the available NPSH is greater than the required NPSHr to avoid cavitation.
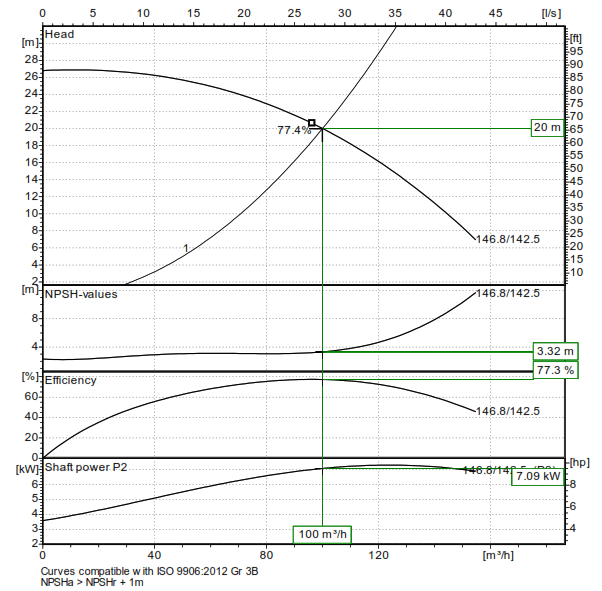
Significance of the Moyno Pump Curve
- Pump Selection:
- Assists in selecting the appropriate pump size and type for specific applications based on flow and head requirements.
- Performance Prediction:
- Enables prediction of how a pump will perform under different operational conditions.
- Troubleshooting:
- Helps diagnose performance issues by comparing actual performance with the pump curve.